Page 41 - USI Newsletter No.94
P. 41
Intelligence 資訊特快車
Express NO.94
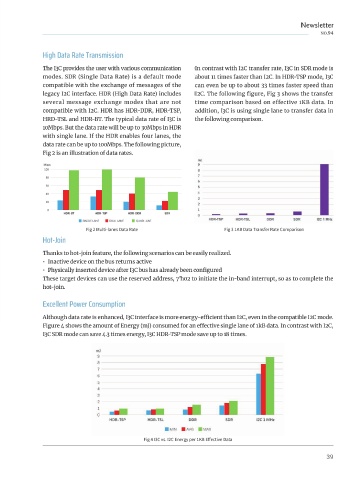
The Introduction of I3C High Data Rate Transmission In contrast with I2C transfer rate, I3C in SDR mode is
The I3C provides the user with various communication
Episode 2 modes. SDR (Single Data Rate) is a default mode about 11 times faster than I2C. In HDR-TSP mode, I3C
compatible with the exchange of messages of the
can even be up to about 33 times faster speed than
legacy I2C interface. HDR (High Data Rate) includes I2C. The following figure, Fig 3 shows the transfer
several message exchange modes that are not time comparison based on effective 1KB data. In
Author: Shanghai Zhangjiang Site / MCS / SAI / Homer Liu
compatible with I2C. HDR has HDR-DDR, HDR-TSP, addition, I3C is using single lane to transfer data in
HRD-TSL and HDR-BT. The typical data rate of I3C is the following comparison.
n the previous issue, we introduced some advantages and the basic framework structure of I3C. Now,
10Mbps. But the data rate will be up to 30Mbps in HDR
let�s take a look at some features of I3C. In practical design and development, these characteristics of I3C with single lane. If the HDR enables four lanes, the
I can provide us with more design ideas and insights. data rate can be up to 100Mbps. The following picture,
Fig 2 is an illustration of data rates.
Now let's dive into some of its cool features.
Two Signal Lines
Two signals, SDA and SCL are adopted. SDA supports both open-drain and push-pull mode. SCL supports push-
pull (avoid power absorption and slow rise-time like I2C), does not support the ability of slaves to stretch the
clock. Push-pull mode achieves I3C high data rate.
In-Band Interrupt
Slave can spontaneously initiate an interrupt. The in-band function allows I3C slave to initiate a START Fig 2 Multi-lanes Data Rate Fig 3 1KB Data Transfer Rate Comparison
transaction whenever they deem it necessary, so as to send its address to master. If more than one slave tries to Hot-Join
access the bus simultaneously, an arbitration will be triggered by the means of the higher priority, the lower Thanks to hot-join feature, the following scenarios can be easily realized.
address. No extra interrupt GPIO is required during the procedure. • Inactive device on the bus returns active
• Physically inserted device after I3C bus has already been configured
In-Band Reset These target devices can use the reserved address, 7'h02 to initiate the in-band interrupt, so as to complete the
Unlike I2C, I3C does not need an extra reset IO to achieve the bus reset. I3C can realize the bus reset by using hot-join.
command code RSTACT. Master can reset one or more selected targets and avoid resetting any others. Abundant
reset levels can achieve different resets ranging from resetting only the I3C peripheral to resetting the whole Excellent Power Consumption
target device. Although data rate is enhanced, I3C interface is more energy-efficient than I2C, even in the compatible I2C mode.
Figure 4 shows the amount of Energy (mJ) consumed for an effective single lane of 1kB data. In contrast with I2C,
I3C SDR mode can save 4.3 times energy, I3C HDR-TSP mode save up to 18 times.
Fig 1 I3C Reset Pattern
Fig 4 I3C vs. I2C Energy per 1KB Effective Data
38 39