Search
- 07/01/2021
The Challenge of Selecting Plastic Material in Mechanical Design
Author: Clive Hsiao /Tooling Development & Material Application Dept. of Central Engineering II (Mechanical)
In mechanical design, the application of material always plays a crucial role, and a proper material selection could make the product satisfy predicted function and secure required quality. Plastic material becomes the most popular selection in mechanical parts due to its excellent processability and less weight property.
How to select Plastic Material
Plastics, belong to polymer, were generally classified as thermoplastics and thermosets. Most of electronic products use engineer plastics such as PA, PC, PC/ABS, POM etc., and some general plastics such as PP, ABS, PMMA. Because of the high cost and extreme molding conditions, seldom parts use high-performance plastics except some internal (special) structural parts.
When we choose plastic material, we will base on product requirements and refer to the material datasheet to select the proper material. The product requirements include mechanical property requirements, user environment requirements, function requirements, 2nd process requirements, cost requirements, and certification requirements etc., general plastic properties including mechanical properties, impact properties, thermal properties, physical properties, electrical properties, flame retardant grade, suggested molding conditions. We could make a comparison table of plastic properties to understand the pros and cons of the plastic materials, then decide the priority of the candidates and arrange trial run verifications.
Furthermore, we should consider the user scenarios and the effects on the product while choosing material. For example, flame retardant materials usually have poor performance on impact strength because it contains more fire retardant additives which drop down the impact property of the material. Another example is that if we added glass fiber to the anti-warping material, it is easy to cause floating fibers on the product's surface and affect the appearance. The enhancement of specific properties on materials is always accompanied by decreasing other properties. Choosing material from a single aspect may lead to the failure of reliability tests or safety certification. The issues caused by wrong material selection always become a disaster because of the difference in shrinkage rate and molding condition between different materials. We usually need to modify tooling, re-make tooling or change design to comply with the new material in the later development phase.
In the past years, from USI’s survey, we found the most common requirement for product plastic material is flame retardant (43%), the second is impact resistance (36%) and follow by anti-warpage (19%). The application of plastics material has become more and more diversified from 2020 regarding environmental awareness and pandemic. The need for antibacterial and post-consumer recycled (PCR) materials is increasing, and biocompatible material is also growing due to wearable device requirement.
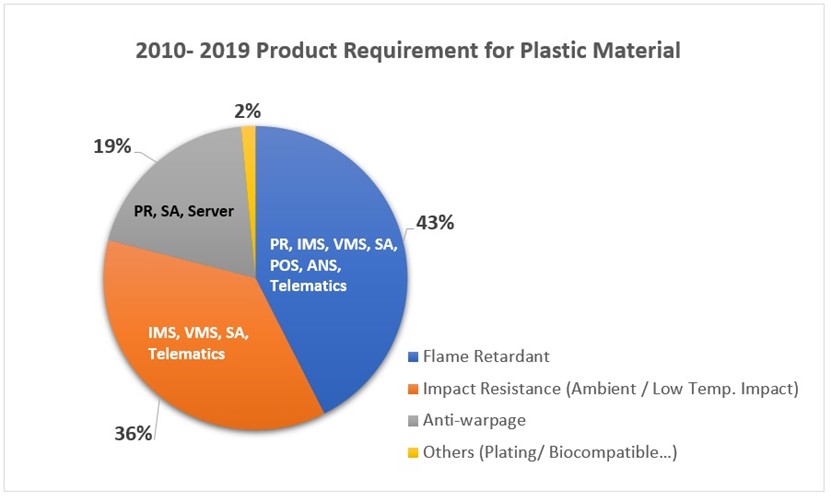
Figure.1 Product Requirement for Plastics Material in Past 10-Year
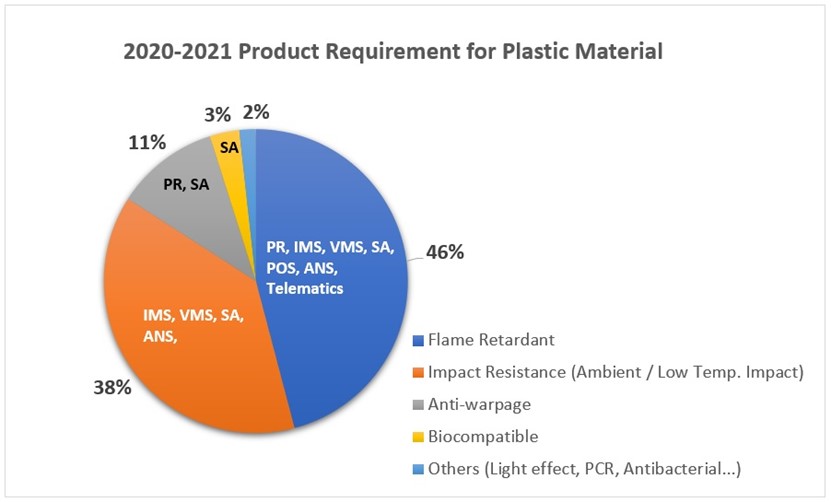
Figure.2 2020~2021 Product Requirement for Plastics Material
The Key Points of Selecting Substitute Plastics Material
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, Texas winter storm, OPEC oil production reduction, and such reasons, many products have faced severe supply shortage issue on plastic material since the end of 2002. We can see the shortage of flame retardant material has a tremendous impact on manufacturing and introduce a substitute material could be an effective solution. We should consider two key points while choosing substitute material:
- The properties of the material such as flame retardant, mechanical properties, and thermal properties should satisfy safety and reliability requirements;
- The molding conditions such as shrinkage rate, flowability, melt temperature, and mold temperature should be close to the original material to reduce molding issues. For example, lower flowability may cause short shot, smaller dimension, or cosmetic issues while molding. If the defects could be solved through adjusting molding condition, it may also lead to material to crack and reduce the mechanical strength. Therefore, it is better to choose the substitute material with flowability similar to the original material. The flowability of material could be obtained via Melt Flow Index (MFI) test, and higher MFI means better flowability.
In addition, we should choose a substitute material that has the same base material as the original resin to avoid colour difference or 2nd process issues. For example, if we select PC as a substitute material, it is challenging to match a similar colour to PC/ABS due to PC is transparent or translucent. At the same time, PC/ABS is Ivory colour in nature.
In conclusion, choosing substitute material will be more strict than choosing material at the initial design phase. Not only the mechanical property needs to have complied with the requirement, but the molding condition also needs to be considered due to the tooling has been done already. It usually requires 1~2 times trial run to verify the product dimension, cosmetic, assembly, and 2nd process. Safety certification and reliability tests are also needed to be applied again.
Keep up with top trending topic
For the latest innovation technology, application
and industry insight.
Subscribe Our Blog
For the latest innovation technology, application
and industry insight.