Search
- 09/18/2024
Internet of Vehicle (IoV) Technology Insight: DSRC & C-V2X
Author: USI WMS Center / Tetsuya Chuang
Continuing with the basic concept in the previous article: “V2X: Revolutionizing Transportation through Vehicle-to-Everything Communication”, I believe you already have a preliminary understanding of “V2X”. The IoV (Internet of Vehicles) is an application of IoT in transportation. By connecting vehicle information and mobile networks, the static and dynamic information of vehicles, pedestrians, and the road environment are identified and transmitted thanks to wireless network communications, data processing, satellite positioning, sensors, and electronic tags effectively. The communication of messages in real-time among the platforms, vehicles, roadside facilities and pedestrians going to facilitate new types of products and services, including traffic safety, transportation service, urban management, logistics and smart toll collecting. In this article, we will take you further into the technology, understand the mainstream specifications in different regions worldwide, and explore more important Know-How in automotive electronics development.
2 Types of IoV Wireless Communication Technology
A standard IoV system consists of wireless communications and applications. The standards for applications are defined by countries or alliances based on regional applications, while the mainstreams of wireless communications in the market are Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) (ITS-G5 for EU) and Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X), both of which are described below:
- DSRC is a V2X technology based on IEEE 802.11p. It is a Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE)/DSRC standard combining IEEE 802.11p and IEEE 1609. The DSRC patents are held mainly through whole car manufacturers or parts and components suppliers in the traditional automotive industry. DSRC is a new technology derived from the traditional automotive industrial chain. It is aimed to improve driving safety and provide stable and reliable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications. It was developed for transportation safety, transportation efficiency, and information service, as shown in Figure 1.
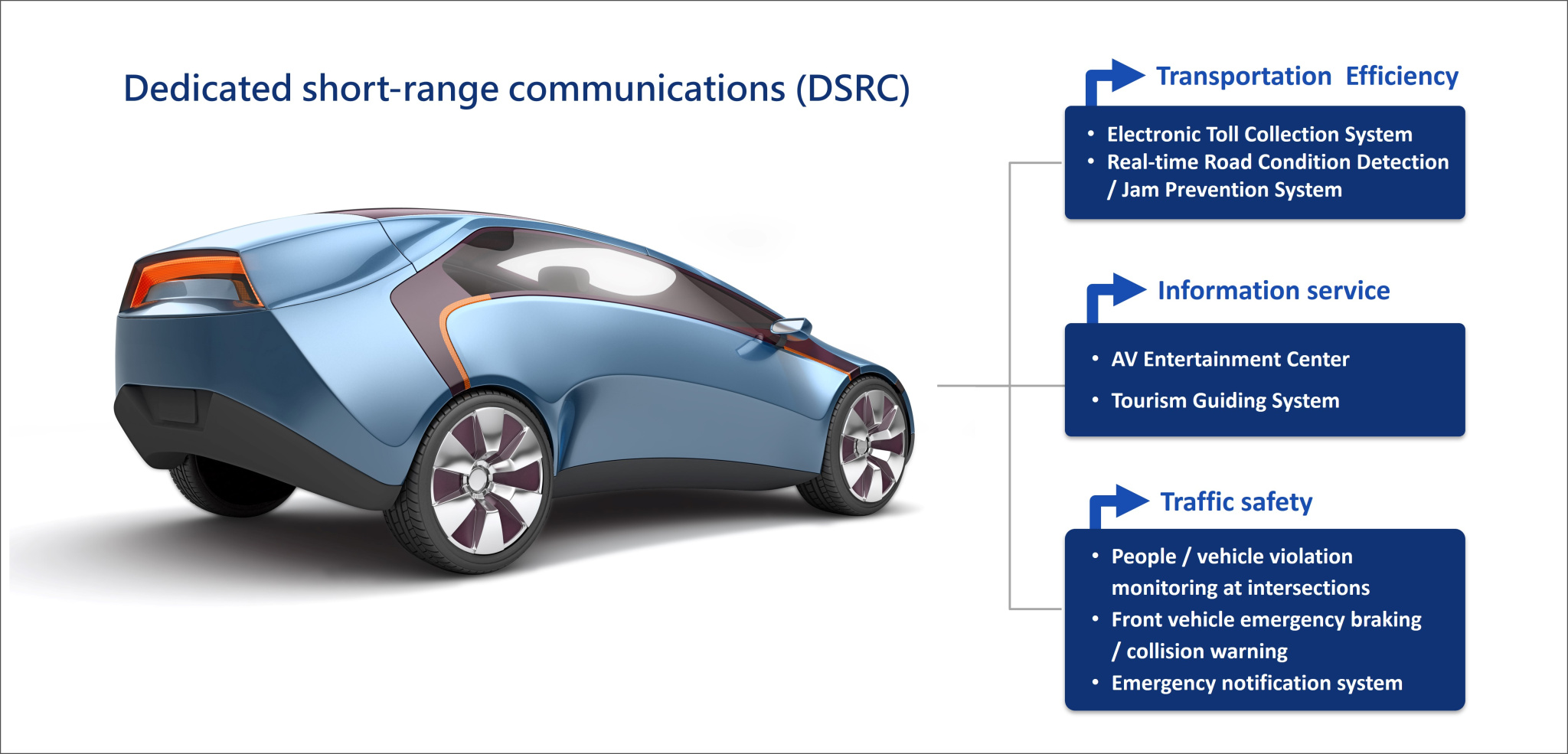
Fig1. Dedicated short-range communications (DSRC)
- Cellular-vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X) specifications were developed in 2015 by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). They start with the Rel-14 standard and consist of service definition, network architecture, and communication techniques. The evolution of C-V2X is presented in Figure 2.
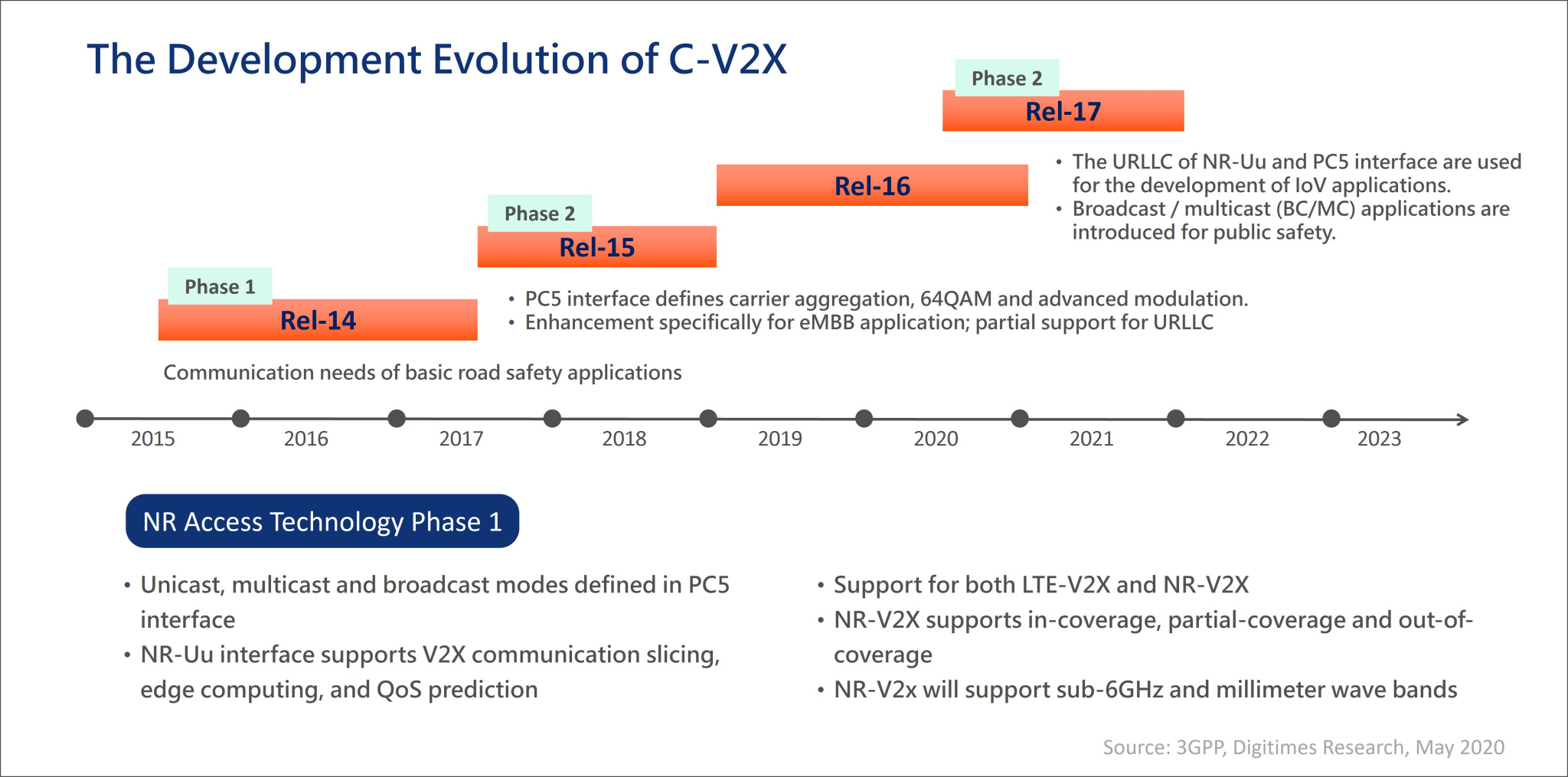
Fig2. The Development Evolution of C-V2X
C-V2X defines two complementary communication modes: one is direct secure communication independent of the cellular network, which realizes direct V2V, V2P, and V2I communications; and the other is that C-V2X allows vehicles to communicate with the V2N network and cloud through the cellular spectra, as shown in Figure 3.
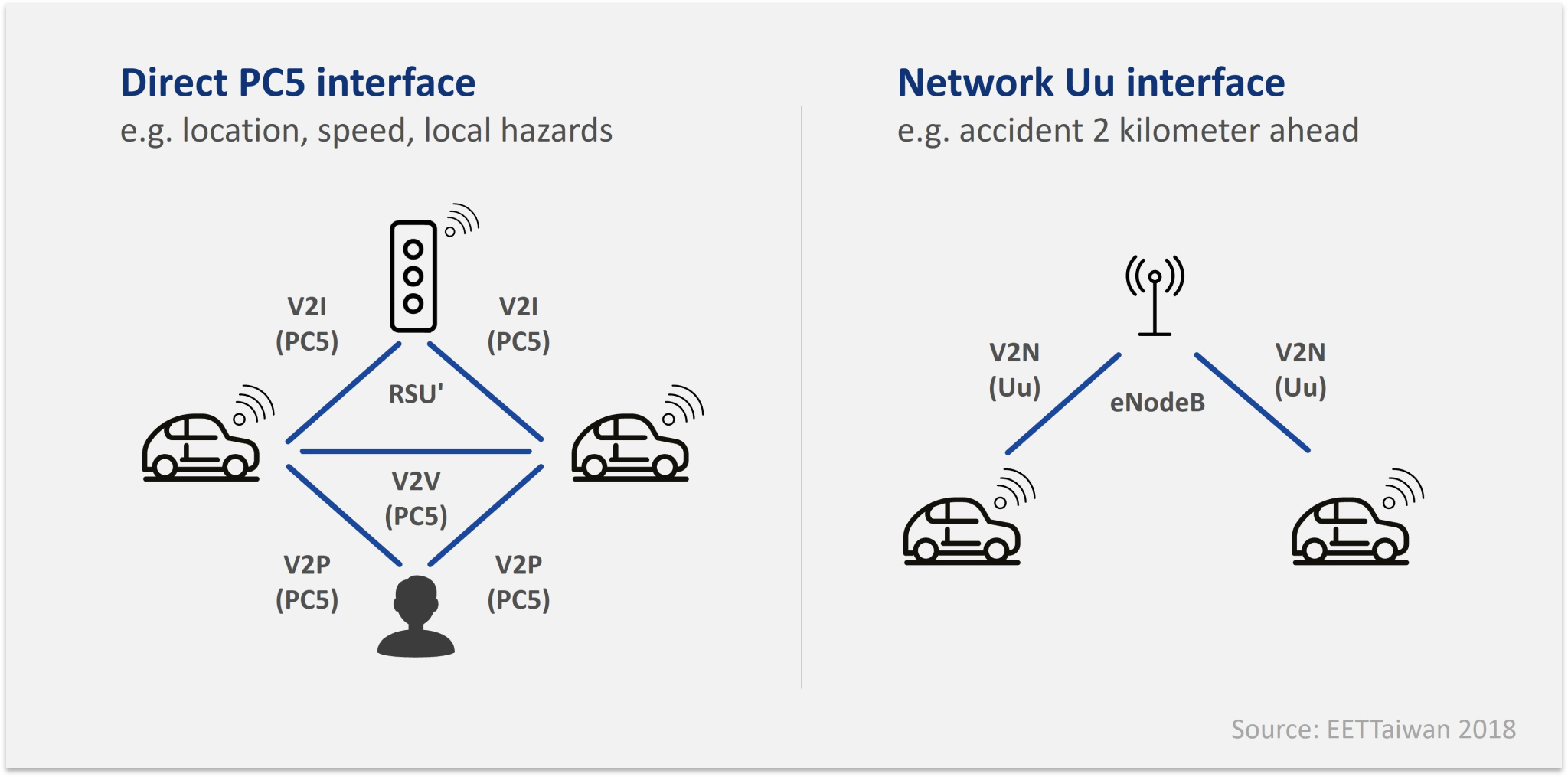
Fig3. C-V2X Communication Modes
Overall, the development of DSRC came earlier and is a relatively new technology derived from the traditional automotive industrial chain. The C-V2X is still in working progress, but it realizes longer-distance communications, greater transmission capacity, quicker response and support for greater travelling speed. It appeals to ICT firms, software service suppliers, and telecommunications operators thanks to its diversified value-adding applications in IoV application services. In addition, the shareability of the 4G/5G network encourages companies to get a head start before C-V2X standards are finalized. The comparison is shown in Table 1.

Table 1. Comparison DSRC vs. C-V2X
IoV Strategies and Outlook for Global Region
Topology Research Institute reported that IoV will take functions to a quantum leap, eventually boosting the number of IoV vehicles. It is projected that up to 80% of new vehicles in 2025 will be equipped with IoV technology, which is to say that 3 out of every 4 new vehicles are capable of IoV.
Therefore, countries around the world are combining their strategies for 5G IoV technology. In addition to taking large steps toward the era of self-driving, they are enthusiastic about the development of related industries and supply chains, and even general consumers are interested in the widespread commercialization.
The following describes the IoV strategies of several major regions, starting with the allocation of spectra, as shown in Table 2:
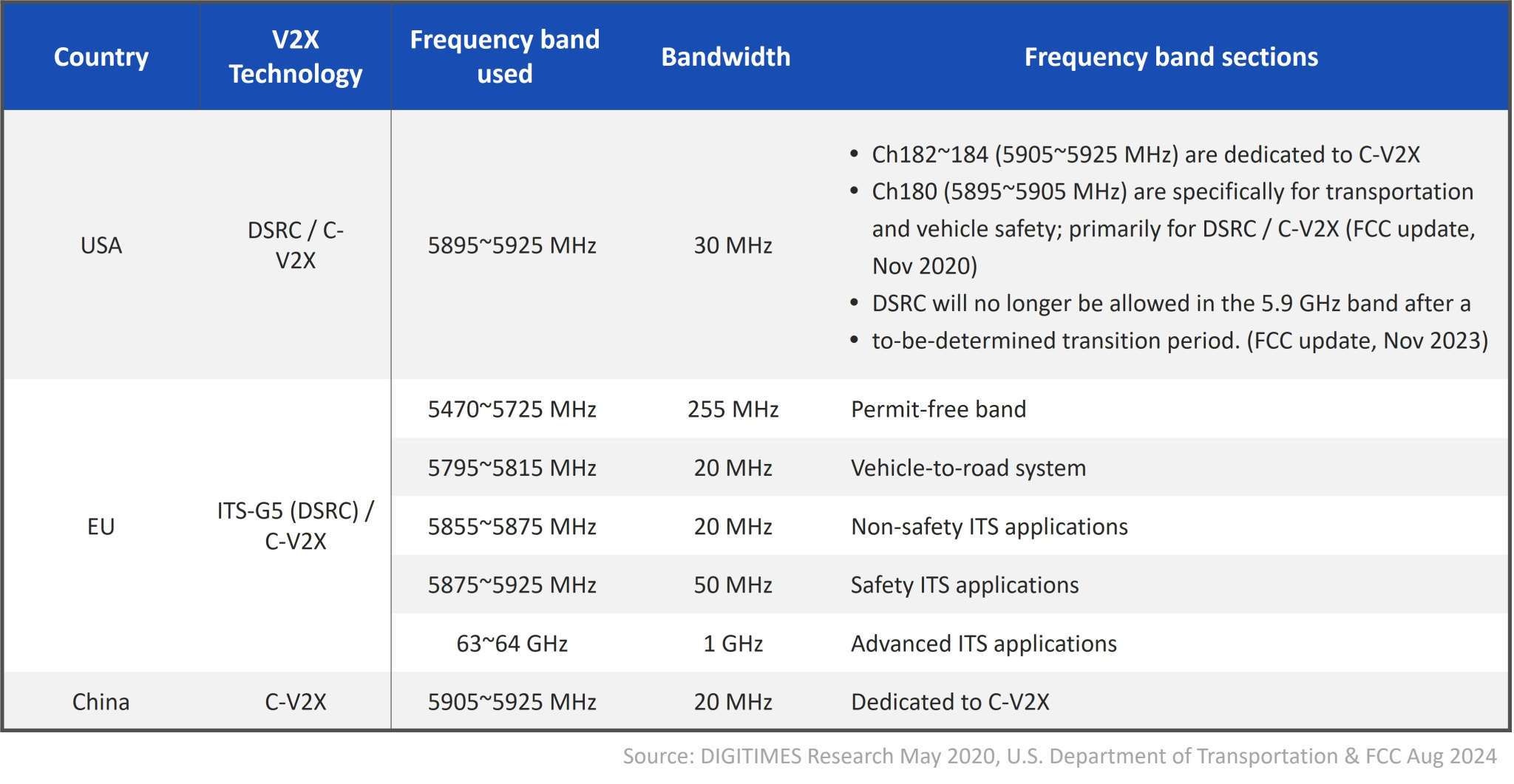
Table 2. Allocation of Spectra in Major Regions
- From the frequency band point of view, the Federal Communication Commission (FCC) rearranged the frequency bands in November 2020. FCC proposed using 45 MHz between 5,850 and 5,895 MHz for unauthorized wireless applications and the reservation of 30 MHz between 5,895 and 5,925 MHz for V2X transportation systems. The band between 5,905 and 5,925 MHz is dedicated to C-V2X, and consideration is given to whether the 10 MHz between 5,895 and 5,905 MHz is assigned to C-V2X or reserved for DSRC. It is not difficult to see that the US is moving from DSRC to C-V2X, which opens the door to introducing 5GC-V2X.
- The EU focuses on both DSRC and C-V2X and established an ITS implementation plan in 2008. In early 2020, the EN 303 613 standard was announced, defining C-V2X as the intelligent transportation system technology, while the ETSI TR 101 607 Cooperative Intelligent Transportation System (C-ITS) was updated to include LTE-V2X.
- China specifies 5.9GHz (5,905~5,925MHz) for the development of C-V2X. According to the C-V2X White Paper of IMT-2020 (5G) Propulsion Group, there are five categories: general technical requirements, introduction level, network level, application level and security, which helps the evolution of IoV from LTE-V2X to 5G C-V2X. Commercialization is realized thanks to integration, testing, infrastructure connection, and verification in various industries. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology announced in 2018 the Management rules for the use of frequency band between 5,905 and 5,925MHz for direct communications of Internet of Vehicle (intelligent network connecting vehicles), allowing regulations and standards to cover lab test standards, equipment establishment standards, protocol specifications and network security.
Intelligent Driving x V2X: The Next Wave of New Blue Oceans
Generally speaking, the days of 5G have come, and the IoT is now the thing. It is expected to see more spectacular development in vertical applications than in the consumer market, and IoV is one of the bright spots that catch everybody’s attention. In the wireless communication technology of the Internet of Vehicles, compared with the use of DSRC technology, a large amount of infrastructure must be built on the roadside so that the deployment cost is significantly increased. The business model is not clear, the development of C-V2X has taken shape, telecom operators do not need to deploy special roadside equipment and provide dedicated spectrum, and its equipment can use the same type of single LTE chipset as mobile phones, which can greatly reduce the integration cost for car manufacturers.
With the development of technology, C-V2X is maturing and becoming an important part of the "intelligent driving" in IoV as the technology develops, while standardization is making good progress. The Chinese government is very active in C-V2X infrastructure and regulation development, and they are leading other regions and expected to take the lead in the next blue sea.
Keep up with top trending topic
For the latest innovation technology, application
and industry insight.
Subscribe Our Blog
For the latest innovation technology, application
and industry insight.